Breast reconstruction surgery aims to rebuild the shape of the breast following a mastectomy or partial mastectomy.
The aim of this procedure is to restore a balanced and normal look in your bra and clothes; however the resulting breast “mound” usually has no nipple and it’s not possible for the surgeon to restore sensation to your breast.
In many (but not all) cases a new nipple can be created surgically once the breast has healed and an areola can be tattooed in place.
In some cases the original nipple may be conserved.
When to have reconstruction
Most women who opt for breast reconstruction have it done at the same time as the initial surgery. This is known as immediate reconstruction.
However, there are often valid reasons why a delayed reconstruction is recommended:
- There is an urgent need for chemotherapy. If chemotherapy treatment needs to be undertaken first, it’s important to wait reconstruction once this has been completed.
- Post-mastectomy radiation will be required. (Radiation treatment can have an adverse effect on cosmetic outcomes).
- Factors such as smoking, diabetes and obesity increase the risk of infection, poor wound healing and other complications and reconstruction may have to be delayed until these risks have been lowered.
- Some women may prefer to have the cancer removed and treated before making any decision about whether to have breast reconstruction.
Many women have a delayed reconstruction by choice, often some years after the original surgery. Unfortunately, in some areas of Guatemala women might experience a long wait to have this done in a public hospital. If you are considering having a delayed reconstruction and are no longer being seen for follow-up at the breast clinic, ask your doctor to refer you to Maria Elena Florido Breast Foundation.
Additional surgeries
With any breast reconstruction, additional surgical procedures may be required to achieve the best cosmetic outcome. Sometimes this might include fat grafting or surgery to the other breast, such as reduction of volume, or a breast lift procedure to achieve symmetry.
What type of reconstruction is best for me?
Recent advances in reconstructive techniques give more choices for breast reconstruction. Each type of breast reconstruction has its own advantages and disadvantages and many factors are taken into consideration when deciding which method is most appropriate for an individual.
Factors to consider are:
- Your general state of health
- The amount of tissue available at potential donor sites
- The impact on your lifestyle and family responsibilities
- The likelihood of radiation therapy being needed
- The length and complexity of various procedures and recovery time
- The desired cosmetic outcome
- Patient and surgeon preference.
The surgeon will advise which procedures are suitable for you. All options may be suitable for some people, while others may have limited options. The choice then rests with you, as only you know which method will fit best with your lifestyle and expectations.
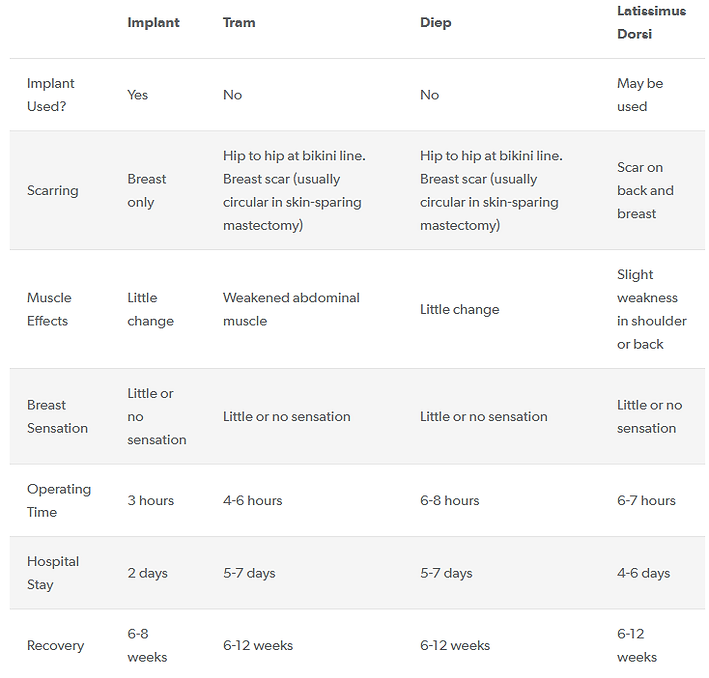
Depending on the type of surgery performed, recovery in hospital is usually between two to seven days requiring a further five to seven weeks to heal. In some cases it may be up to 12 weeks.
There are two main types of breast reconstruction:
- Implant reconstruction
- Autologous/autogenous reconstruction (using your own tissue)
Sometimes a combination of these two methods is used.
1. Implant Reconstruction
This involves inserting a silicone breast implant underneath the skin and the muscle of the chest wall after the breast tissue has been removed. A tissue-expansion process is commonly needed first to create a cavity for the implant and gradually stretch the skin.
2. Autologous /autogenous reconstruction (Reconstruction procedures that use your own tissue)
These procedures are complex and require a longer hospital stay and longer recovery time than implant reconstruction. There is significant scarring at the donor site and when muscle is used it may result in weakness at the donor site, but the use of natural tissue results in a breast more natural look and feel.